Blockchain technology is at the heart of almost every cryptocurrency; it is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger for securely recording transactions across a network of computers.
Transparency, immutability, and trust emerge without the need to involve intermediaries like banks.
Each “block” is assigned a record of transactions, which is then linked to the rest of the blocks, thus making it almost impossible to change old transactions.
This technology makes cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum function, giving individuals secure, tamper-proof mechanisms for transferring value online.
This guide will delve into the fundamentals of blockchain technology, how it works, its applications, and its implications for various industries.
What is Blockchain?
Fundamentally, a blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that keeps track of transactions across several computers in a way that makes it impossible to change the recorded transactions later.
Each block of the chain contains a list of transactions, and as a block is loaded with information, it is connected to the block before it, creating a chronological chain.
Key Characteristics of Blockchain
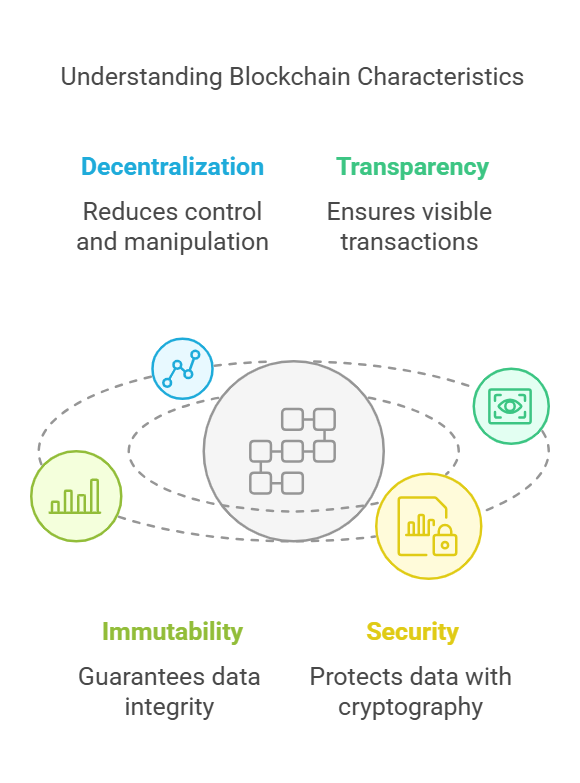
- Decentralization: Blockchains are decentralized unlike traditional databases controlled by a central authority. No single person has complete control over the enormous network, which is encouraging as it reduces the risk of deception and manipulation.
- Transparency: Every blockchain transaction is transparent to all network participants. This transparency builds confidence and accountability among users.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain and confirmed by the network, it cannot be changed or removed. This immutability ensures the integrity of the data.
- Security: Blockchain uses cryptography techniques to protect data. Transactions are encrypted, and each block is appended to the previous one using a cryptographic hash function. This makes it incredibly difficult for bad actors to change the data.
How Does Blockchain Work?
To understand how blockchain works, it’s important to break down its components and processes:
1. Blocks
Each block contains three main elements:
- Data: This includes the transaction details, such as the sender, receiver, and amount.
- Nonce: A nonce is a one-time use random number that miners must find to produce a new block.
- Hash: A cryptographic hash function creates a unique identifier for the block. It consists of the previous block’s hash, which links them together.
2. Nodes
Many nodes form a blockchain network, that is, different computers that carry a copy of the chain. Each node validates and verifies transactions before adding it to the blockchain.
3. Consensus Mechanisms
Blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms to agree on the validity of transactions and add new blocks to the chain. The most common mechanisms are:
- Proof of Work (PoW): In the case of Bitcoin, miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. The first miner to solve the puzzle adds the block and receives a cryptocurrency reward.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In this system, validators (or “stakers”) create a newer number of blocks based on the number of coins they control and the quantity they stake. This method is more energy-efficient than PoW.
4. Mining
Mining is the process by which new blocks are created and added to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve mathematical problems that validate transactions. When a block is successfully mined, the blockchain adds it, and the miner receives a reward, typically in the form of cryptocurrency.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
While blockchain is most commonly associated with cryptocurrencies, its applications span various industries:
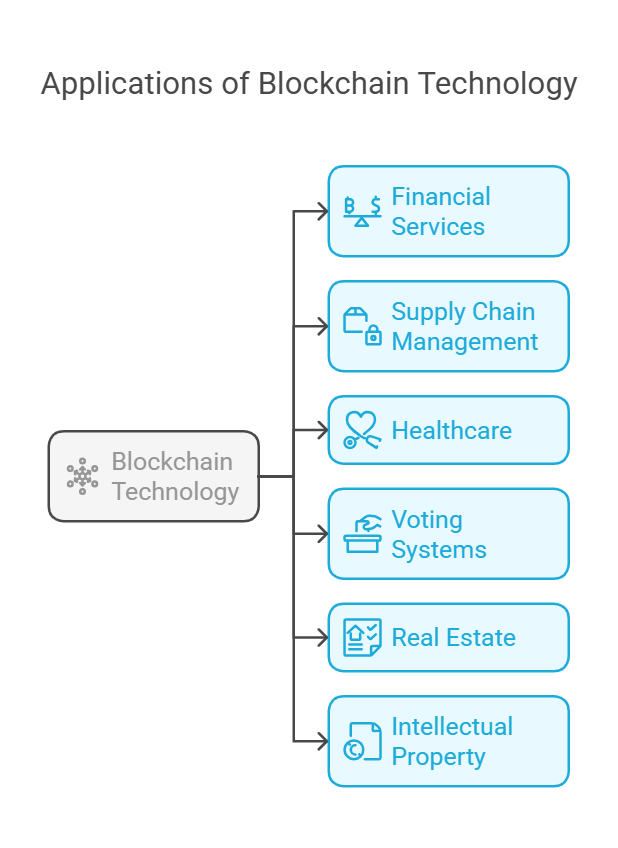
1. Financial Services
Blockchain technology can revolutionize the financial sector by enabling faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions. It allows real-time settlement of transactions while reducing the need for intermediaries, such as banks.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can improve transparency and traceability in supply chains. By recording every transaction on a blockchain, companies can track the movement of goods from origin to destination, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
3. Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, blockchain can securely store patient records, ensuring they are immutable and accessible only to authorized personnel. This can improve patient care and data accuracy while protecting patient privacy.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent platform for voting. By recording votes on a blockchain, the process can become tamper-proof, ensuring the integrity of elections and increasing public trust in the electoral process.
5. Real Estate
Blockchain can streamline property transactions by enabling smart contracts that automate the transfer of ownership. This reduces the need for intermediaries and expedites buying and selling.
6. Intellectual Property
Creators can use blockchain to secure their intellectual property rights. By recording their work on a blockchain, they can establish proof of ownership and protect their creations from unauthorized use.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges:
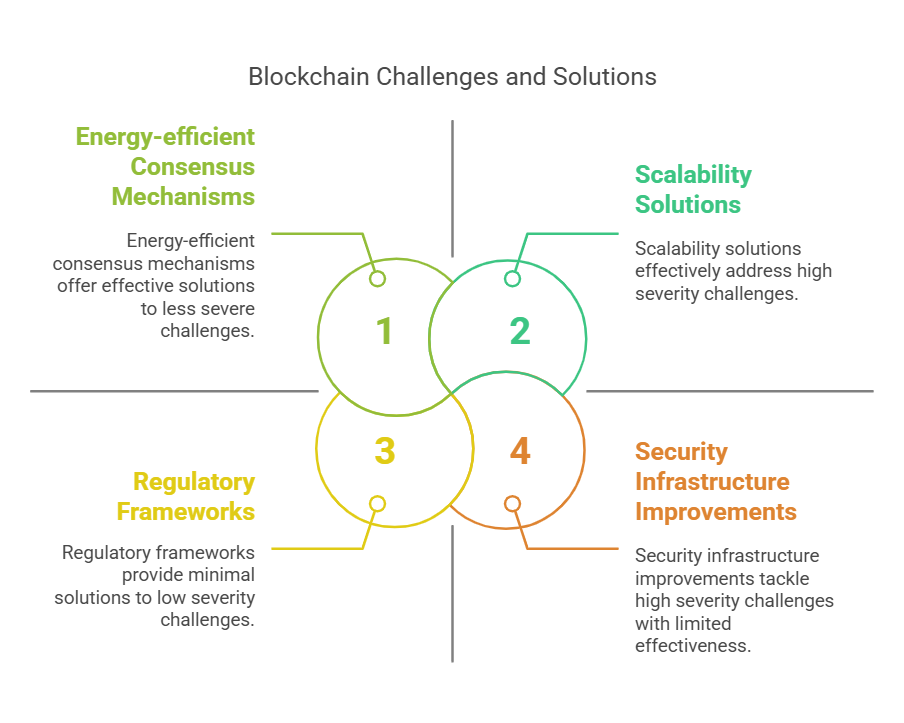
1. Scalability
As the number of transactions increases, many blockchain networks struggle to process them quickly. Solutions such as layer-two scaling and sharding are being explored to improve scalability.
2. Energy Consumption
Proof of Work, the consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin, requires substantial energy to mine new blocks. This has raised concerns about its environmental impact. Alternatives like Proof of Stake aim to address these concerns by being more energy-efficient.
3. Regulatory Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies remains unclear in many jurisdictions. Governments are still determining how to classify and regulate blockchain technology, which can hinder its adoption.
4. Security Concerns
While blockchain is secure, vulnerabilities exist in the surrounding infrastructure, such as wallets and exchanges. Hacks and scams targeting these platforms can lead to significant losses for users.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
The future of blockchain technology looks promising. As industries recognize its potential, investment, and research into blockchain solutions are increasing. Here are some trends to watch:
1. Increased Adoption
More businesses are beginning to adopt blockchain technology for various applications, from supply chain management to finance. This trend is likely to continue as the benefits of blockchain become more apparent.
2. Interoperability
As the number of blockchain networks grows, the need for interoperability between different blockchains becomes crucial. Initiatives to create cross-chain solutions will facilitate communication between various networks.
3. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi applications are gaining popularity, allowing users to borrow, lend, and trade cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. The DeFi ecosystem is rapidly expanding, demonstrating the potential of blockchain technology in finance.
4. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs have emerged as a new way to represent ownership of unique digital assets. As the NFT market grows, blockchain technology will play a vital role in verifying ownership and authenticity.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a transformative force that extends far beyond cryptocurrency. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature has the potential to revolutionize various industries, offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges.
While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and increased adoption indicate a bright future for blockchain. Understanding how this technology works and its applications can help individuals and businesses navigate the evolving landscape of digital assets and decentralized systems.
As we continue to explore the possibilities of blockchain, its impact on our lives and industries will only become more profound.
